The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC) has raised concerns over the escalating impact of Lassa fever, as the virus continues to spread across an increasing number of states and communities.
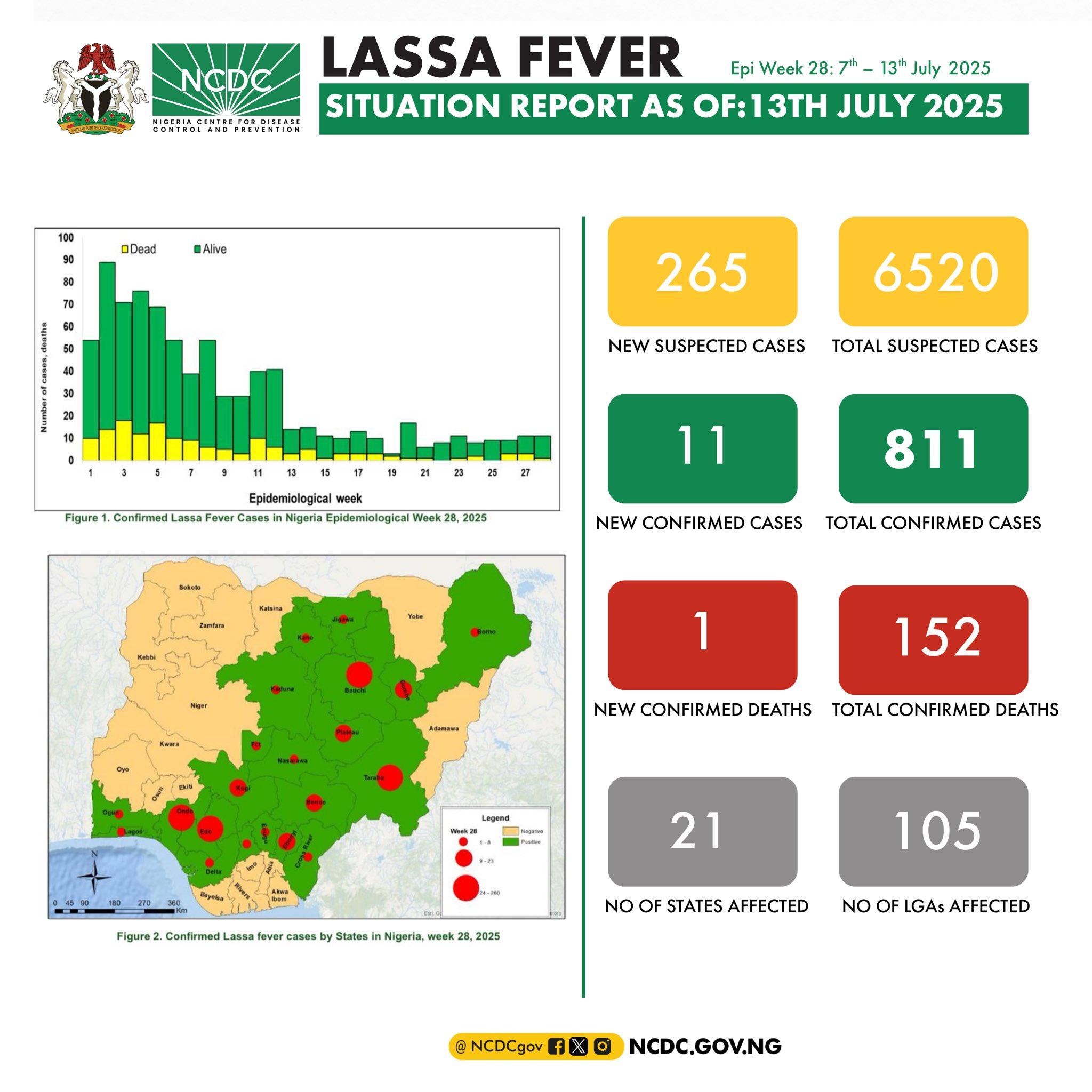
According to the latest Lassa Fever Situation Report for Epidemiological Week 28 (7th–13th July 2025), the country has recorded 152 deaths from 811 confirmed cases across 21 states and 105 Local Government Areas (LGAs).
This has brought the Case Fatality Rate (CFR) to a troubling 18.7%.
The NCDC noted that this marks a worrying increase compared to the same period in 2024, which recorded 940 confirmed cases and 163 deaths across 28 states, with a CFR of 17.3%.
“While the number of suspected and confirmed cases has slightly decreased this year, the higher fatality rate signals the continued severity of the disease.”
During the reporting week alone, 265 suspected cases were documented, with 11 confirmed and one death recorded in Ondo, Edo, and Benue States.
These states remain among the most affected, with Ondo leading by contributing 32% of all confirmed cases in 2025.
Other high-burden states include Bauchi (23%), Edo (17%), Taraba (14%), and Ebonyi (3%). Together, these five states account for 89% of all confirmed infections nationwide.
Lassa Fever Update – Week 28, 2025
🗓 7th–13th July📍11 new confirmed cases in Ondo, Edo & Benue
📊 Total for 2025:
✅ 811 confirmed cases
✅ 152 deaths
✅ CFR: 18.7% (↑ vs 17.3% same time in 2024)
🔹 89% of cases from Ondo, Bauchi, Edo, Taraba & Ebonyi— NCDC (@NCDCgov) July 28, 2025
The most affected age group is between 21 and 30 years, although confirmed cases range from infants to the elderly (aged 1 to 96 years).
The male-to-female ratio among confirmed cases stands at approximately 1:0.8.
In response, the National Lassa Fever Technical Working Group (TWG), coordinated by the NCDC, has intensified control measures using a multi-sectoral and multi-partner approach.
Recent interventions include:
- Deployment of 10 National Rapid Response Teams to affected states
- Clinician training in Bauchi, Ebonyi, and Benue, supported by WHO
- Launch of the second cohort of the Lassa Fever Clinical Management Fellowship
- Strengthening of surveillance and active case search in communities and health facilities
- Public sensitisation via media campaigns and targeted community engagement
- Distribution of thermometers, PPEs, Ribavirin, hand sanitisers, and IEC materials
- Environmental hygiene campaigns and rodent control activities
- Implementation of clinical trials and After-Action Reviews in key states
- Enhancement of laboratory testing and data analysis capacity for faster diagnosis
Notably, no new infections among healthcare workers were reported in Week 28, although 23 healthcare personnel have been infected in total this year.
Despite intensified efforts, the NCDC highlighted ongoing challenges, which include:
- Late presentation of cases at health facilities, increasing the risk of death
- Poor health-seeking behaviour, often due to high treatment costs
- Low awareness and unsanitary living conditions in many affected communities
The NCDC is urging Nigerians—particularly those in high-burden states—to remain vigilant and adopt key preventive measures, such as:
- Keeping living areas clean and rodent-free
- Avoiding direct contact with rodents
- Seeking prompt medical attention if symptoms like fever, vomiting, or unexplained bleeding occur
Both the public and healthcare professionals are advised to access detailed guidance and resources via the NCDC website or call the toll-free line: 6232 for accurate and timely information.
For more updates:
🌐 www.ncdc.gov.ng
📧 info@ncdc.gov.ng
🐦 Twitter: @NCDCgov

