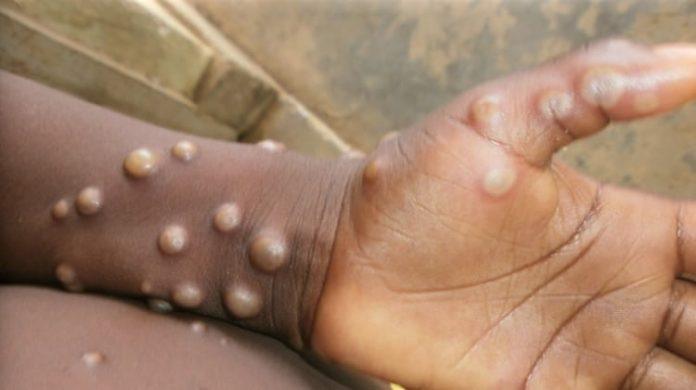
Africa has recorded more than 61,383 mpox cases and 296 deaths across 32 countries since early 2024, as continent-wide efforts to develop effective treatment options gain momentum.
The Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) disclosed this in a statement in Abuja, Nigeria’s Capital.
- Read more: Africa CDC Reports Gains In Mpox Response
The statement followed the announcement of a collaboration agreement between Emergent BioSolutions and the Pandemic Preparedness Platform for Health and Emerging Infections Response (PANTHER) to provide additional financial support for the Africa CDC-led Mpox Study in Africa (MOSA).
Launched in 2024, the MOSA initiative is a double-blind, platform-adaptive clinical trial designed to evaluate potential treatment options for patients diagnosed with mpox across multiple African countries.
The Director-General of Africa CDC, Dr Jean Kaseya, described the study as a critical step towards strengthening Africa’s capacity to respond to emerging and re-emerging public health threats.
“This study represents a significant step in generating evidence to inform mpox treatment and strengthen Africa’s capacity to respond to emerging health threats,” Kaseya said.
An independent Data and Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB) completed its initial review of MOSA safety data in December 2025, after the first 50 patients were randomised, and recommended continuing the trial, with no safety concerns identified.
Dr Simon Lowry, Chief Medical Officer and Head of Research and Development at Emergent BioSolutions, said the company was proud to support the trial’s advancement.
“We commend Africa CDC, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) investigators and PANTHER for reaching this important milestone and remain committed to collaborating with research partners to address global health threats,” Lowry said.
The study, which initially received funding from the European Union and Africa CDC, has so far focused largely on the DRC, one of the countries most affected by mpox outbreaks. Africa CDC and PANTHER plan to expand the trial to additional countries, including Uganda, as enrolment continues.
Africa CDC noted that the continent is affected by both major mpox clades: Clade I, which is endemic to Central Africa and associated with more severe illness, and Clade II, which is more prevalent in West Africa. Recent outbreaks have also involved subclades such as Clade Ia, Ib, IIa and IIb.
NAN